In today’s interconnected world, student exchange programs have become a vital pathway for global learning and cross-cultural engagement. These programs allow students to study abroad for a limited time, typically one semester to one academic year, while remaining enrolled at their home institution. This article explores the core concept of exchange programs, their unique features, common types, differences from full-time degree study abroad, the general application process, and the best countries to consider for a successful exchange experience.
Ⅰ. What Is an Exchange Student Program?
An exchange student program is a temporary academic arrangement in which a student from one institution (the "home" university) studies at a partner institution abroad (the "host" university) under a reciprocal agreement. Unlike full-time international study, exchange students typically do not transfer permanently—they study abroad for a specific duration, earn transferable credits, and return to complete their degree at home.These programs aim to promote international understanding, foster academic collaboration, and provide students with the opportunity to experience different educational systems and cultures.
Ⅱ. Key Features of Exchange Student Programs
1. Reciprocal Agreements:
Exchange programs are based on mutual partnerships between universities or educational organizations, meaning students are "exchanged" without additional tuition costs at the host school.
2. Temporary Duration:
Exchanges usually last from one semester to a full academic year, offering a taste of international life without the long-term commitment.
3. Credit Transferability:
Courses taken abroad are typically pre-approved and count toward the student’s degree requirements back home.
4. Cultural Immersion:
Beyond academics, exchange students live among local peers, engage with new customs, and often stay with host families or in student dormitories, gaining firsthand insight into another way of life.
5. Support Services:
Both home and host institutions provide guidance on course selection, visas, accommodation, and adjustment to ensure a smooth experience.
![]()
Ⅲ. Common Types of Exchange Programs
1. University-to-University Exchange:
The most common type, where two partner universities allow students to swap places, often waiving tuition at the host institution.
2. Government-Sponsored Programs:
Programs such as Erasmus+ (Europe), JASSO (Japan), and the U.S. Fulbright or YES Abroad offer structured exchange opportunities, often with financial support and cultural activities.
3. High School Exchange:
Students aged 15–18 study at a foreign secondary school, typically through organizations like AFS or Rotary Youth Exchange.
4. Short-Term or Summer Programs:
These offer condensed study abroad experiences—often language or culture-based—lasting from a few weeks to a few months.
Ⅳ. Exchange vs. Full-Time Study Abroad
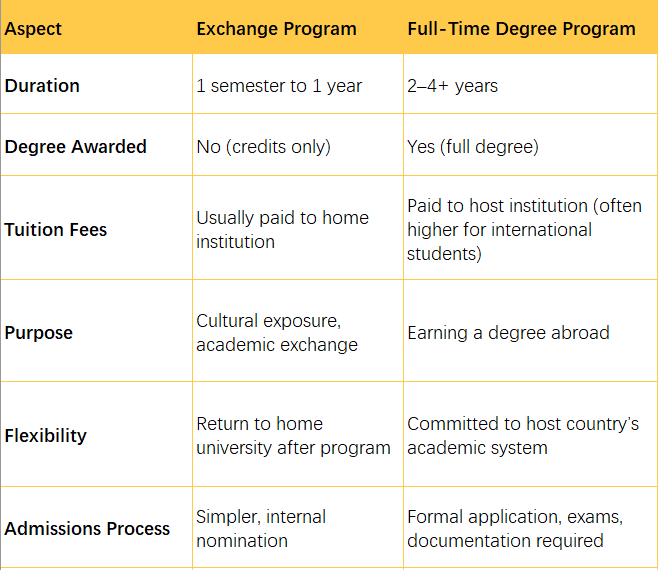 Ⅴ. How to Apply for an Exchange Program
Ⅴ. How to Apply for an Exchange Program
1. Research Available Programs
Start with your home university’s international office or website. Look at partner schools, eligibility requirements, and course offerings abroad.
2. Check Eligibility Criteria
Requirements may include a minimum GPA, language proficiency (e.g., TOEFL, JLPT), and completion of a certain number of credit hours.
3. Prepare an Application Package
Usually includes a personal statement, transcripts, recommendation letters, and a study plan or learning agreement.
4. Undergo Nomination and Selection
Many programs require you to be nominated by your home institution before applying to the host.
5. Submit Required Documents to Host Institution
Once accepted, you’ll need to finalize your application with the host university and possibly apply for housing or student services.
6. Apply for a Student Visa
Based on the host country’s regulations, visa requirements may include proof of enrollment, finances, insurance, and vaccinations.
7. Attend Pre-Departure Orientation
Most schools offer sessions to prepare you culturally and logistically for the upcoming exchange.
Ⅵ. Benefits of Becoming an Exchange Student
1. Global Perspective
Studying abroad exposes you to different worldviews, political systems, and cultural norms, making you a more informed and open-minded individual.
2. Language Proficiency
Living in a different linguistic environment accelerates your ability to speak, listen, and think in a new language.
3. Academic Enrichment
You’ll experience different teaching styles, take courses unavailable at your home institution, and expand your intellectual flexibility.
4. Personal Growth
Living independently in a new country builds resilience, confidence, and problem-solving skills.
5. Career Advantage
Employers value international experience, intercultural communication skills, and adaptability—all gained through exchange programs.
6. Lifelong Friendships
Exchange students often build strong relationships with peers from around the world, creating global networks that last a lifetime.
The exchange student program is a rewarding way to enhance your education, broaden your cultural horizons, and prepare for a global future. It offers flexibility, academic value, and unforgettable personal experiences—all without the long-term commitment or high cost of a full-time degree abroad. Whether you’re aiming to boost your career, master a new language, or simply see the world from a different perspective, an exchange program may be your perfect first step.